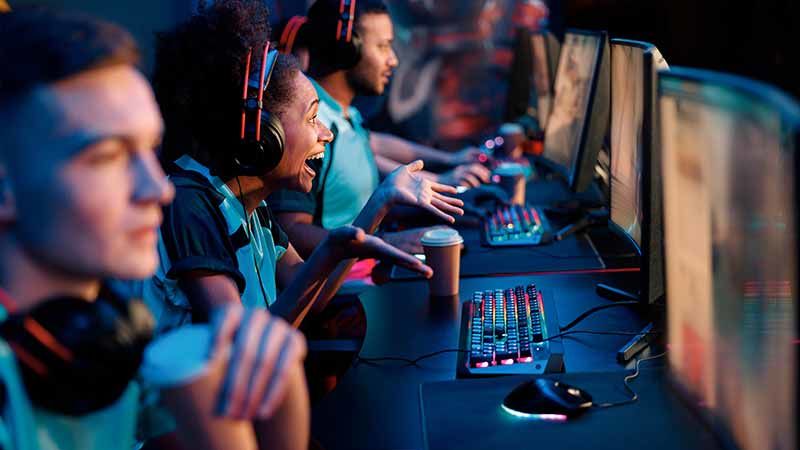
The rapid evolution of technology has given rise to a phenomenon that has captured the hearts and minds of millions: electronic sports, or e-sports. What was once a niche activity has now blossomed into a global sensation, drawing audiences that rival traditional sports events. In this article, we will delve into the world of e-sports and competitive gaming, exploring their origins, growth, significance, and the unique ecosystem they have fostered.
The Rise of E-sports:
1. Origins and Evolution:
- E-sports trace their roots back to the early days of video gaming and LAN parties, where gamers would gather to compete against each other locally.
2. Global Popularity:
- E-sports have gained immense popularity worldwide, with major tournaments, leagues, and championships attracting millions of viewers both online and in person.
3. Diverse Game Titles:
- E-sports encompass a wide range of game genres, from multiplayer online battle arenas (MOBAs) like League of Legends and Dota 2 to first-person shooters like Counter-Strike: Global Offensive and battle royales like Fortnite and PUBG.
4. Professional Players and Teams:
- E-sports have given rise to a new generation of professional players, who train rigorously, compete at the highest levels, and earn substantial incomes through sponsorships and prize winnings.
E-sports Ecosystem:
1. Esports Organizations:
- Professional teams and organizations invest in player training, infrastructure, and brand building. These entities create a sense of community and competition within the e-sports landscape.
2. Sponsorships and Endorsements:
- Companies from various industries sponsor e-sports teams and events, promoting their brands to a tech-savvy and engaged audience.
3. Streaming and Content Creation:
- Platforms like Twitch and YouTube enable players to stream their gameplay, interact with fans, and generate income through ads and subscriptions.
4. E-sports Events:
- Major e-sports tournaments, such as The International for Dota 2 and the League of Legends World Championship, draw massive live audiences and viewership online.
The Significance of E-sports:
1. Community and Inclusivity:
- E-sports create a global community where players from diverse backgrounds connect, compete, and share a passion for gaming.
2. Skill, Strategy, and Teamwork:
- Competitive gaming requires strategic thinking, lightning-fast reflexes, and teamwork, challenging players to hone their skills and adapt to dynamic situations.
3. Professionalization of Gaming:
- E-sports have transformed gaming into a legitimate career path, with players, coaches, analysts, and content creators contributing to the industry’s growth.
4. Future Prospects:
- The e-sports industry continues to expand, with increasing investment, recognition, and mainstream integration, pointing toward a bright future.
E-sports and competitive gaming represent a cultural and technological revolution that has redefined entertainment, competition, and community engagement. As e-sports continue to evolve and captivate audiences around the world, they illuminate the potential of digital platforms to unite individuals, nurture talents, and foster a sense of camaraderie. With each epic match, spectacular play, and thrilling competition, e-sports solidify their place in the modern landscape, shaping a new era of sports and entertainment that resonates with digital natives and enthusiasts alike.
Challenges Faced by Game Developers: Navigating the Complex World of Game Production
The world of game development is a dynamic and ever-evolving landscape, marked by creativity, innovation, and the pursuit of virtual realms that captivate players. Behind every immersive gaming experience lies a team of dedicated developers who bring these digital worlds to life. However, the road to game creation is not without its challenges. In this article, we will delve into the myriad difficulties that game developers encounter as they strive to produce captivating and memorable gaming experiences.
1. Technological Complexity:
- Game developers grapple with the continuous advancement of technology, striving to optimize graphics, physics, and gameplay mechanics while ensuring compatibility across various platforms and devices.
2. Time and Resource Constraints:
- Meeting deadlines and managing limited resources can be a significant challenge, particularly for indie developers or smaller studios with budget constraints.
3. Creative Pressure:
- Balancing innovation and market demand is a delicate task. Developers often face the challenge of creating unique and engaging gameplay while also catering to player expectations.
4. Quality Assurance:
- Ensuring a bug-free and polished gaming experience requires rigorous testing, debugging, and optimization, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
5. Monetization and Business Models:
- Choosing the right monetization strategy, such as free-to-play, premium, or microtransactions, while maintaining player satisfaction and fairness, can be a complex decision.
6. Market Competition:
- The gaming industry is highly competitive, with thousands of games released annually. Standing out and attracting players in a saturated market is a constant challenge.
7. Player Engagement and Retention:
- Keeping players engaged and invested in a game over the long term requires continuous updates, content expansions, and community engagement.
8. Cultural and Regional Sensitivity:
- Game developers must navigate cultural differences and sensitivities to ensure that their games are inclusive and avoid unintentionally causing offense.
9. Crunch Culture and Burnout:
- The pressure to meet deadlines can lead to extended work hours and burnout among developers, highlighting the need for a healthier work-life balance.
10. Technical Limitations: – Developers often face technical constraints, such as hardware limitations, that may impact the scope and ambition of their projects.
11. Intellectual Property and Legal Issues: – Navigating copyright, licensing, and intellectual property issues can be complex, especially when creating original content inspired by existing works.
12. Adaptation to Player Feedback: – Reacting to player feedback and balancing the desire for game improvements with maintaining the core vision of the game can be challenging.
Game development is a multifaceted endeavor that demands creativity, technical prowess, and resilience. The challenges faced by game developers are diverse and encompass technical, creative, business, and ethical considerations. Despite these hurdles, the passion and dedication of game developers drive them to overcome obstacles, create exceptional gaming experiences, and contribute to an industry that continues to push the boundaries of entertainment and technology. As the world of gaming evolves, so too do the challenges and opportunities that shape the creation of immersive virtual worlds.