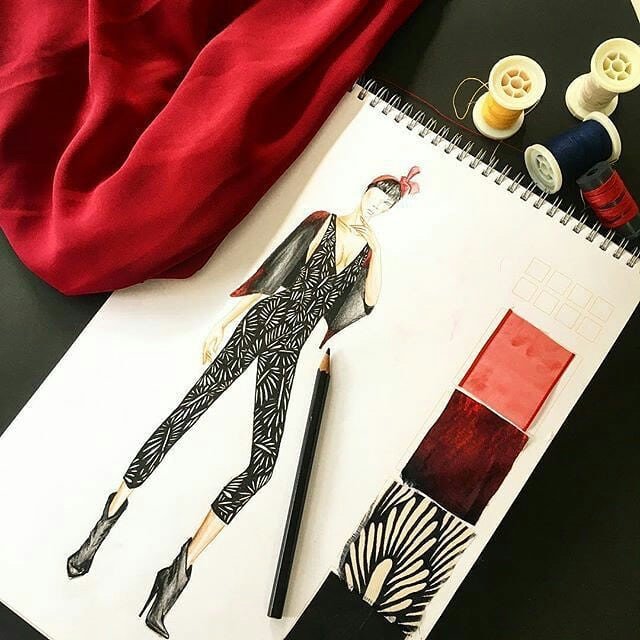
Fashion design education plays a pivotal role in shaping aspiring designers into innovative and skilled professionals. This article explores the structure, curriculum, and significance of fashion design education programs, shedding light on how these programs cultivate creativity, technical proficiency, and industry-relevant skills. By delving into various aspects such as course offerings, industry partnerships, and experiential learning, this article aims to provide insights into the dynamic realm of fashion design education and its contribution to the ever-evolving world of fashion.
Introduction: Fashion design education programs are instrumental in nurturing the next generation of creative minds in the fashion industry. This article examines the components and impact of these programs, emphasizing their role in honing talents and preparing students for successful careers in fashion design.
Curriculum and Course Offerings:
- Foundation Courses: Fundamental courses in design principles, color theory, and textiles provide a strong conceptual base.
- Technical Skills Development: Courses in pattern-making, draping, and sewing impart essential technical expertise.
- Specialized Workshops: Workshops on digital design tools, sustainable practices, and trend analysis equip students with current industry knowledge.
Creative Exploration and Conceptualization:
- Concept Development: Students learn to ideate, conceptualize, and translate their creative visions into tangible designs.
- Portfolio Development: Crafting a diverse and strong portfolio is emphasized, showcasing a range of design skills and personal style.
Industry Engagement and Partnerships:
- Internships: Collaboration with fashion houses, brands, and design studios offers real-world experience and industry exposure.
- Guest Lectures: Industry professionals provide insights into market trends, entrepreneurship, and successful design practices.
Experiential Learning:
- Fashion Shows and Exhibitions: Organizing fashion shows and exhibitions allows students to showcase their collections and gain public recognition.
- Design Competitions: Participation in design competitions hones skills, fosters healthy competition, and boosts visibility.
Sustainability and Ethical Practices:
- Incorporating Sustainability: Programs integrate sustainable design principles, reflecting the industry’s growing emphasis on ethical practices.
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Students are encouraged to explore eco-friendly materials and production methods.
Technological Integration:
- Digital Design Tools: Teaching students to use computer-aided design (CAD) software enhances design precision and efficiency.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): Incorporating VR and AR technologies offers new dimensions to design visualization.
Multidisciplinary Exposure:
- Cross-Disciplinary Collaboration: Collaborative projects with other design fields like textiles, accessories, and jewelry encourage diverse creative exploration.
- Global Perspective: Exposure to international design influences and cultural diversity enriches students’ design sensibilities.
Fashion design education programs serve as a launchpad for emerging designers, fostering creativity, technical mastery, and industry awareness. By offering a comprehensive curriculum, industry engagement, experiential learning, and a commitment to sustainability, these programs prepare students to navigate the dynamic world of fashion with innovation, professionalism, and a deep understanding of design aesthetics. As the fashion industry continues to evolve, the role of fashion design education remains vital in shaping the trends and creative forces that shape the global fashion landscape.
The Future of Fashion: Trends, Innovations, and Sustainable Evolution
The fashion industry is undergoing a transformative journey, driven by changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, and a growing emphasis on sustainability. This article explores the emerging trends, innovations, and sustainable practices that are shaping the future of fashion. By examining concepts such as circular fashion, digitalization, AI-driven design, and ethical production, this article aims to provide insights into the dynamic and promising path that the fashion industry is charting for the years ahead.
Introduction: The fashion landscape is in a state of flux, influenced by societal shifts and technological breakthroughs. This article delves into the multifaceted future of fashion, unraveling the forces driving change and the exciting possibilities that lie ahead.
Sustainable Revolution:
- Circular Fashion: A shift towards circular models emphasizes recycling, upcycling, and reducing waste, resulting in longer-lasting garments.
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Innovative materials like sustainable fabrics, bio-fabrics, and lab-grown textiles contribute to a greener fashion ecosystem.
Technological Disruption:
- Digitalization: Virtual showrooms, online retail experiences, and digital fashion showcases redefine the consumer engagement journey.
- 3D Printing: Customizable and efficient, 3D printing revolutionizes garment production and allows for unique design possibilities.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-driven design tools aid in trend forecasting, design creation, and personalization, enhancing efficiency and creativity.
Personalization and Individual Expression:
- Mass Customization: Technology enables personalized fashion, where consumers can design and customize their garments to reflect their unique style.
- Digital Avatars: Virtual avatars enable consumers to visualize clothing items, fostering a new era of personalized shopping experiences.
Ethical and Transparent Practices:
- Fair Labor: Conscious consumerism drives demand for ethically produced garments, ensuring fair wages and safe working conditions.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Blockchain technology enables traceability, allowing consumers to verify the origins and authenticity of products.
Localism and Global Collaboration:
- Local Production: A resurgence of local craftsmanship and manufacturing supports sustainable practices and reduces carbon footprint.
- Cross-Cultural Collaborations: Global design collaborations celebrate diversity and offer fresh perspectives on fashion aesthetics.
Innovations in Retail:
- Augmented Reality (AR) Fittings: Virtual try-ons and AR-enhanced shopping offer a personalized and interactive retail experience.
- Contactless Payments: The rise of contactless and digital payments streamlines transactions and enhances convenience.
Gender Fluidity and Inclusivity:
- Gender-Neutral Fashion: An evolving mindset challenges traditional gender norms, leading to more inclusive and fluid fashion choices.
- Inclusive Sizing: Brands embracing diverse body types and offering inclusive sizing reflect a more inclusive and body-positive approach.
The future of fashion is a tapestry woven with innovation, sustainability, and consumer empowerment. As the industry embraces circular practices, technology-driven solutions, ethical production, and a heightened focus on individual expression, it evolves into a dynamic force for positive change. By embracing these trends and championing sustainability, fashion is poised to not only redefine style but also contribute to a more responsible, inclusive, and forward-looking global culture.